It is arguably the most exciting non-event in recent economic history.
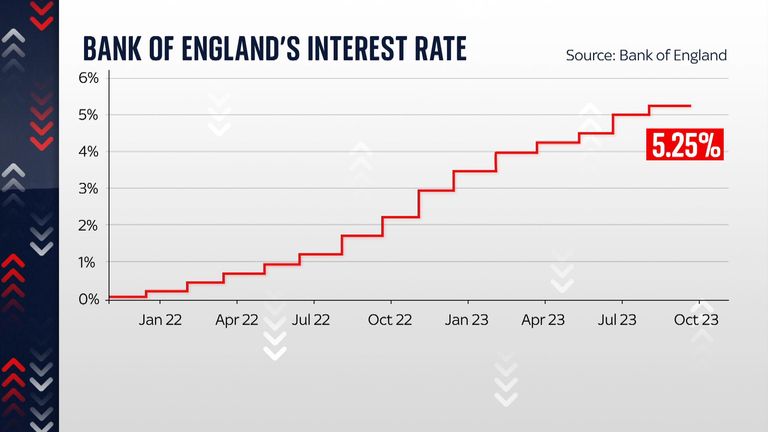
For 14 successive monetary policy meetings, the Bank of England raised its official interest rate – all the way from 0.1% up to 5.25%.
Today, for the first time since late 2021, it voted to leave borrowing costs unchanged.
Reaction to BoE’s decision – latest updates
Now in some senses, this is indeed a non-event. The Bank interest rate is no higher than it was yesterday, but the cost of borrowing remains painfully high for many households.
Those due to refinance their mortgages in the coming months will still see a sharp increase in their rates compared with two or five years ago. The cost of living crisis is still with us.
And this gets to a critical point underlying the Bank’s thinking. In much the same way as a fall in inflation doesn’t mean the cost of living crisis is over – prices are still rising fast, but not quite as fast as previously – freezing interest rates doesn’t mean the impact they have will diminish.
Indeed, at their current level, the Bank believes that interest rates should be considered “restrictive” – so even keeping the Bank rate at 5.25% is delivering medicine to the economy, bearing down on spending and, the Bank hopes, inflation.
Even so, today’s decision is the most convincing signal yet that the Bank may now be close to, or even at, the peak for the interest rate. The decision today was so finely balanced that many will wonder whether it will still go ahead and hike the rate at its next meeting.
But in leaving borrowing costs where they are, the Bank is following a similar path to the European Central Bank – which just raised rates but hinted that might be that – and the Federal Reserve, which also left US rates on hold earlier this week. All around the world, central banks are coming to the conclusion that they may now be at the peak for interest rates.
But that raises a further question: what now? Investors are betting that the Bank may start cutting borrowing costs as soon as next year. But insiders at Threadneedle Street aren’t so sure. They suspect rates may have to stay higher for longer, both to bring inflation down and to ensure it stays down. Moreover, they warn that the days of zero interest rates may be gone for good.