Heat pumps are becoming more popular for residential housing with energy prices increasing and the need to reduce use of fossil fuel heating systems.
Andrew Aitchison | In Pictures | Getty Images
In case you haven’t noticed, heat pumps are hot. Although these devices, which use electricity to generate both air conditioning and heat, have been around for decades, the latest models are much more efficient and cost-effective alternatives to conventional fossil-fuel furnaces and air conditioners.
But there are other reasons why heat pumps are fast becoming popular with homeowners. The federal government, as well as an increasing number of states, are offering consumers attractive tax credits and rebates for buying and installing heat pump systems as a way to reduce climate-warming greenhouse gas emissions and propel the transition to renewable energy.
All of this is transforming Carrier Global, the nearly 100-year-old manufacturer whose founder, Willis Carrier, invented air conditioning. Over the past year, the Palm Beach Gardens, Florida-based company has been repositioning itself to capitalize on the fast-growing market for heat pumps and other sustainable heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) technologies.
“We all know that sustainability is a megatrend,” Carrier Global Chairman and CEO David Gitlin told a group of investors in February. “HVAC has to have a critical seat at the table.”
After being spun off from United Technologies — its parent since 1979 — in 2020, and then divesting several non-HVAC businesses, Carrier made its biggest bet yet on the heat pump boom when it acquired Germany’s Viessmann Climate Solutions for roughly $13 billion last April. In addition to proprietary heat pump technology, Viessmann offers renewable energy capabilities and home battery storage, as well as smart home system controls and applications that can be integrated to drive energy efficiency.
“HVAC is at an inflection point right now, with a tremendous shift toward electrification, going from fossil fuel-burning boilers and furnaces to heat pumps,” said Hakan Yilmaz, Carrier’s chief technology and sustainability officer. “In addition, the cooling side of HVAC is expected to triple by 2050, because 2.8 billion people live in hot climate zones and only about 8% have access to HVAC today,” he said. The massive scale and massive consumption of the energy resiliency issue, Yilmaz says, puts the HVAC industry in a position to capitalize.
Heat pumps have a history dating back to 1850s
The thermodynamic science behind heat pumps was developed in the 1850s, when the first ones were invented, and they’ve been used in homes since the 1960s. Heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat from a cool space to a warm space, making the cool space cooler and the warm space warmer. Many of today’s models are three to five times more efficient than fossil-fuel furnaces, and work well even in extremely cold and hot weather.
The most common type is the air-source heat pump system, comprising an outdoor unit — which resembles a conventional central AC device — and an indoor unit that hooks up to either a blower that circulates warm or cool air through ducts and vents or to one or more ductless mini-splits installed in rooms throughout a house.
14 February 2024, Saxony, Leipzig: Michael Kretschmer (r, CDU), Minister President of Saxony, talks to Viessmann employee Sebastian Kowalski about a heat pump at the Haus-Garten-Freizeit trade fair. Kretschmer takes part in the East Trade Policy Forum.
Picture Alliance | Picture Alliance | Getty Images
Compared to a gas boiler, heat pumps reduce GHG emissions by 20% when operating on fossil fuel-generated electricity and as much as 80% when operating on cleaner electricity, according to the International Energy Agency. Residential and commercial buildings account for 30% of global energy consumption and produce 26% of energy-related GHG emissions, per the IEA.
In 2023, air-source heat pumps outsold fossil-fuel furnaces for the second year in a row, according to AHRI, the trade association representing HVAC manufacturers. Rewiring America, a nonprofit advocate for mass-scale electrification, estimates that currently, 16% of U.S. homes use heat pumps for heating and cooling. In September, the U.S. Climate Alliance, a bipartisan coalition of 25 governors, agreed to collectively reach 20 million heat pump installations by 2030, with the aim of ensuring at least 40% of benefits flow to disadvantaged communities.
In the U.S., so far cold states are leading the way
Although heat pumps have become popular for air conditioning in southern states, Maine has the highest rate of adoption, installing 100,000 units in households two years ahead of schedule and aiming to hook up another 175,000 by 2027. That dispels the notion, often promulgated by the oil and gas industry and utilities, that heat pumps don’t work well in below-freezing temperatures, thus requiring a fossil-fuel furnace as backup.
“That’s old news,” said Tobie Stanger, senior home and appliances writer for Consumer Reports. “There are new heat pumps designed for cold weather that allow them to go to five degrees effectively,” she said, adding that they’re widely used in Nordic and European countries. A Consumer Reports analysis of the efficacy of heat pumps in cold climates found that “even amid bone-chilling cold” they use far less energy than other types of heating systems. According to Dave Lis, director of technology market transformation at Northeast Energy Efficiency Partnerships (NEEP), air-source heat pumps can work as a home’s main heating system in almost any climate.
Carrier sells 10 different heat pumps, with various energy capacities and price points, and plans to add models made by Viessmann, which already has a presence in the U.S. market. But beyond the company’s sustainable energy technology and product portfolio, “one of the reasons we acquired Viessmann was because of its experience in training dealers and installers and helping customers understand the benefits of its products,” said Milena Oliveira, Carrier’s chief marketing and communications officer.
Leveraging that knowledge, Carrier is providing its nationwide network of around 2,100 authorized dealers training and education programs, as well as advertising and promotional support, not only regarding heat pumps but also ancillary products, such as smart thermostats and energy storage batteries. “Home energy management is a huge component that we want to capitalize on,” Oliveira said, as dealers “shift their mindsets from selling products to selling solutions and components.”
Mark Prodan, the operations manager of M&M Plumbing and Heating, a Carrier dealership in the northern Michigan town of Indian River, said that M&M’s heat pump business grew by nearly 35% last year. “This year it will probably be up another 40% to 50%,” he said.
Prodan said that he typically has to educate customers about the energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness of heat pumps, as well as their environmental benefits. “There’s a general feeling that people want to go with a little bit cleaner energy, but once you educate them on what heat pumps can do, they’re usually very receptive,” he said.
Carrier on-site and remote training of M&M’s sales and service staff have helped, Prodan said. “They have a website with knowledge-based videos, calculators that show customers their cost savings and an app for our service guys that can scan a bar code to pull up information and manuals.”
Getting tax credits and rebates while they last
Between now and the end of 2032, homeowners can get a 30% federal tax credit for the purchase and installation of Energy Star-certified air-source heat pumps — from Carrier and other brands — up to $2,000 annually. That includes any related insulation, ducting, mini-splits and electricity upgrades.
Many states and local utilities offer additional financial incentives, some tied to income levels. Connecticut, for instance, offers a rebate of up to $15,000 for qualifying heat pumps; New York State issues rebates through utility companies that can amount to between $8,000 and $12,000; Maine offers between $4,000 and $8,000. The Energy Star website features a “rebate finder” for obtaining information by zip code.
The cost of installing a heat pump system — depending on the brand, size, where you live and complexity of the job — can be upward of $20,000. Consumer Reports member surveys found that the overall median price paid for the purchase and installation of a ducted heat pump between 2018 and 2023 was $8,348. Mini-splits can range from $2,000 to $6,000 per unit, plus installation.
Besides rebates and tax credits, heat pumps can generate savings by eliminating the cost of fossil fuels, even when factoring in the price of electricity. Rewiring America calculated that homeowners switching from inefficient HVAC systems that run on fuel oil, propane or traditional electric resistance (like baseboard heat or electric furnaces) can save around $1,000 per year.
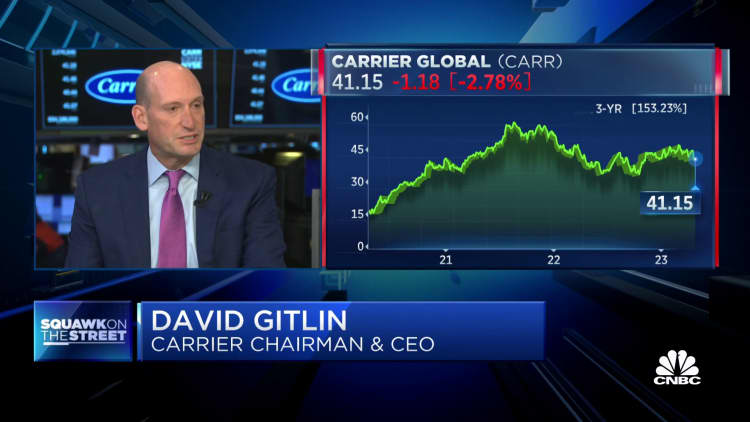
For 2023, Carrier reported sales of $22.1 billion, up 8% from $20.4 billion in 2022. Its guidance for 2024 projected sales growing to $26.5 billion. The stock is up 30% over the past year, though it is stalled in 2024.
Loading chart…
“This is a big year for us as a company,” Gitlin said in a recent call with analysts. “We will start realizing the tremendous benefits from the combination of Viessmann and as a sustainability-focused, higher growth, pure-play company.”
“When I see companies making big changes to their [product] portfolio and divestitures, that puts a premium on management knowhow and capability,” said Deane Dray of RBC Capital Markets. “I like how they’re doing it,” he said. “The heat pump [focus] does not just make economic sense, but the impact on its carbon footprint is a good part of the story as well.”
Carrier is targeting net-zero GHG emissions in its own operations by 2030 and across its value chain by 2050. The recent stock retreat, Dray says, doesn’t concern him and over the longer term, he anticipates higher margins, more services and more aftermarket revenues. “It’s all lining up nicely,” he said.





![Daimler CEO just dropped some pretty WILD pro-hydrogen claims [update]](https://i0.wp.com/electrek.co/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2025/09/hydrogen_semi.jpg?resize=1200,628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)






